How the Forex Market Works: Key Players & Structure
The foreign exchange market better known as Forex or FX is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world. With over $7.5 trillion traded daily, it’s a global powerhouse that never sleeps. But how exactly does it work? And who are the key players moving all that money around?
In this post, we’ll break down the structure of the Forex market and introduce you to the major players involved in every transaction, from governments to retail traders.
What Is the Forex Market?
The Forex market is where currencies are bought, sold, and exchanged. Unlike the stock market, which has centralized exchanges like the NYSE, Forex is decentralized and operates over-the-counter (OTC) meaning there’s no physical location or central authority.
It functions 24 hours a day, five days a week, across major financial hubs:
- Sydney opens first
- Followed by Tokyo
- Then London
- And finally, New York
This global loop creates continuous trading activity, allowing people to buy and sell currencies at any time.
How Forex Trading Works
In Forex, you trade currency pairs buying one currency while simultaneously selling another. For example, when you trade EUR/USD, you’re buying Euros while selling U.S. dollars.
The goal? To profit from the change in the exchange rate between the two currencies.
Forex trading relies on a combination of supply and demand, economic indicators, and market sentiment, all of which can move prices by the second.
🧩 The Structure of the Forex Market
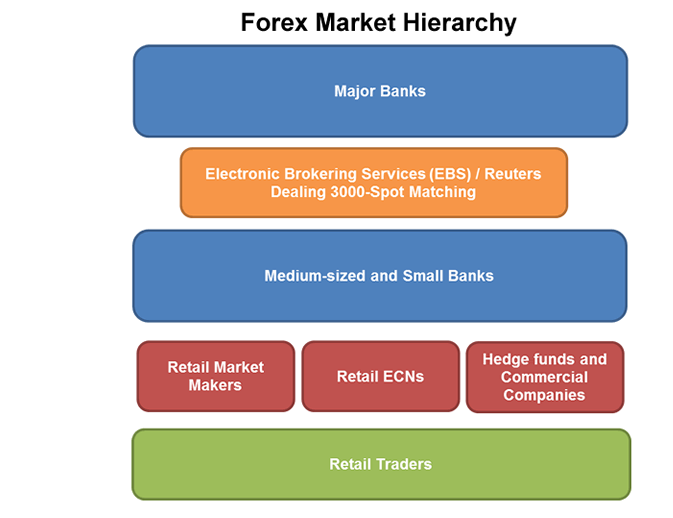
The Forex market is structured into tiers or levels. Here’s how it’s organized:
1. Interbank Market (Top Tier)
This is where the biggest players trade large amounts of currency directly with each other.
Includes:
- Central banks (like the U.S. Federal Reserve, ECB)
- Global commercial banks (JPMorgan, Citibank, HSBC)
- Investment banks and financial institutions
Features:
- Extremely high volume trades
- Tightest spreads (difference between buy/sell prices)
- Access limited to institutions
2. Liquidity Providers and Prime Brokers
They act as middlemen, offering liquidity and pricing to smaller institutions, hedge funds, and high-volume traders.
Roles:
- Aggregate prices from interbank participants
- Provide pricing and execution to brokers
- Offer margin and credit facilities
3. Retail Forex Brokers
These brokers connect everyday traders (like you and me) to the Forex market.
Two types:
- Dealing Desk Brokers (Market Makers): Take the opposite side of your trade and often create their own pricing.
- No Dealing Desk Brokers (STP/ECN): Route your trades directly to the larger market (more transparent pricing).
Popular platforms: MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), cTrader
4. Retail Traders (Bottom Tier)
This includes individual investors trading from home or through apps and platforms. Thanks to technology and leverage, retail traders now make up a significant portion of daily trading volume.
Retail trader advantages:
- Low barriers to entry
- Demo accounts for practice
- High leverage options (but risky)
- Access to global currencies
🧠 Who Are the Key Players in Forex?
Let’s dive into the roles of major participants:
✅ 1. Central Banks
They manage monetary policy, set interest rates, and sometimes intervene in currency markets to stabilize their economy.
Example: The U.S. Federal Reserve raising interest rates can strengthen the U.S. dollar.
✅ 2. Commercial Banks
They facilitate Forex transactions for clients and also engage in speculation and hedging.
Examples: JPMorgan Chase, Deutsche Bank, Barclays
✅ 3. Corporations
Businesses involved in international trade use Forex to convert earnings or hedge against currency risk.
Example: An exporter in Europe receiving USD payments will convert them to EUR.
✅ 4. Hedge Funds & Investment Firms
These players trade large volumes using complex strategies, often influencing short-term price movements.
✅ 5. Forex Brokers: How the Forex Market Works: Key Players & Structure
Act as intermediaries for retail traders, offering platforms, leverage, and execution services.
✅ 6. Retail Traders: How the Forex Market Works: Key Players & Structure
You and millions of others using platforms to trade currencies based on market analysis, news, and strategies.
How Are Forex Prices Determined?
Prices in the Forex market are influenced by a variety of factors, including:
- Supply and demand
- Interest rate differentials
- Economic indicators (GDP, unemployment, inflation)
- Political stability or instability
- Market sentiment and news events
These factors create a dynamic and ever-changing market where no single entity controls the prices.
Final Thoughts: How the Forex Market Works: Key Players & Structure
Knowing how the Forex market is structured and who the key players are gives you a strategic edge as a trader.
It helps you: How the Forex Market Works: Key Players & Structure
- Recognize market trends and why they’re happening
- Understand liquidity and volatility during different sessions
- Choose the right broker based on your trading style
- Avoid unrealistic expectations and risky leverage traps
Forex is a powerful financial tool—but it requires knowledge, practice, and discipline. Understanding how the market operates is the first major step on your journey.