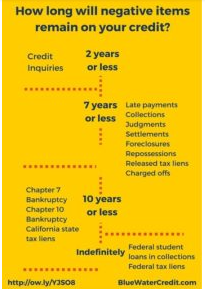
How Long Does Negative Information Stay on Your Credit Report?
If you’ve ever missed a payment, defaulted on a loan, or faced bankruptcy, you know the sinking feeling of wondering: How long will this stay on my credit report? The good news is, negative information doesn’t last forever. Over time, it will fall off your report, and its impact on your credit score lessens as you rebuild positive history.
Let’s break down how long different types of negative information remain on your credit report and what you can do in the meantime.
Why Negative Information Matters
Your credit report is a record of how you’ve managed debt in the past. Lenders, landlords, and even insurance companies use it to decide if you’re a reliable borrower. Negative marks can lower your score, limit your opportunities, and cost you more money in higher interest rates.
But here’s the key: time heals credit wounds.
How Long Different Negative Marks Stay on Your Report
1. Late or Missed Payments
-
Duration: Up to 7 years from the date of the missed payment.
-
Even one late payment can hurt, but the impact lessens if you return to making on-time payments consistently.
2. Accounts in Collections
-
Duration: Up to 7 years from the date the account first went delinquent.
-
Paying off a collection may not erase it immediately, but some newer scoring models (like FICO 9 and VantageScore 4.0) give less weight to paid collections.
3. Charge-Offs
-
Duration: 7 years from the date the account became delinquent.
-
A charge-off happens when a lender gives up on collecting payment and writes the account off as a loss—but it still stays on your record.
4. Foreclosures
-
Duration: 7 years.
-
Losing a home through foreclosure is serious, but it won’t haunt your credit forever.
5. Bankruptcies
-
Chapter 7 Bankruptcy: Up to 10 years.
-
Chapter 13 Bankruptcy: Up to 7 years (since you repay part of your debts).
6. Hard Inquiries
-
Duration: 2 years (though they usually stop affecting your score after about 12 months).
-
These occur when lenders check your credit for applications like loans or credit cards.
7. Student Loan Defaults
-
Duration: Typically 7 years from the date of default (though federal student loan rules can vary).
Do Negative Marks Affect Your Score the Whole Time?
Not equally. While negative information stays on your report for years, its impact fades as it ages—especially if you practice good credit habits in the meantime. For example:
-
A late payment from last month hurts more than one from five years ago.
-
Building new positive history (on-time payments, low balances) can offset older mistakes.
How to Rebuild After Negative Information
Even if you have negative marks, you’re not stuck forever. Here’s how to recover:
-
Pay bills on time going forward (payment history is the #1 factor in your score).
-
Lower your credit utilization by paying down balances.
-
Dispute inaccuracies on your credit reports.
-
Consider secured credit cards or credit-builder loans to add positive history.
Final Thoughts
Negative information on your credit report can feel discouraging, but it doesn’t last forever. Most marks fall off after seven years, and their sting weakens with time. By focusing on building healthy credit habits now, you can bounce back stronger and position yourself for better financial opportunities in the future.
Remember: your credit score tells your financial story—but you’re the author of the next chapter.