How Interest Rates Work: Fixed vs. Variable Explained
When it comes to borrowing money whether for a home, car, or personal expenses interest rates play a critical role in how much you’ll actually pay over time. But not all interest rates are the same. The two most common types are fixed and variable interest rates, and understanding the difference between them can save you thousands of dollars.
In this post, we’ll break down how interest rates work, the difference between fixed and variable rates, and how to decide which one is right for you.
What Is an Interest Rate?
An interest rate is the cost of borrowing money, expressed as a percentage of the loan amount (principal). Lenders charge interest to compensate for the risk of lending and the loss of access to that money over time.
For example, if you borrow $10,000 at an annual interest rate of 5%, you’ll pay $500 per year in interest—on top of repaying the original loan amount.
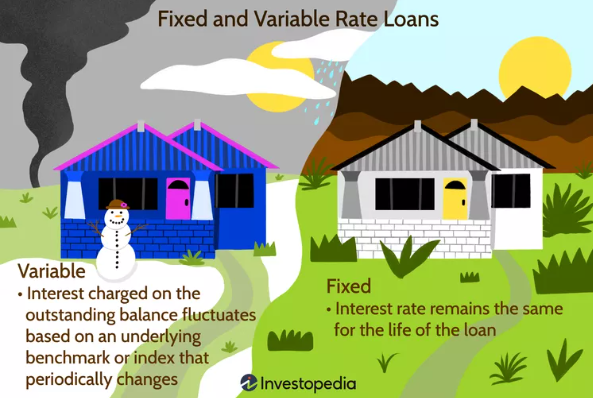
🔒 What Is a Fixed Interest Rate?
A fixed interest rate stays the same for the entire term of your loan. That means your monthly payments won’t change, making it easier to budget.
✅ Pros:
-
Predictable monthly payments
-
Protection from rising interest rates
-
Great for long-term planning
⚠️ Cons:
-
May start higher than variable rates
-
Less flexibility if market rates drop
Best for:
-
Mortgages
-
Auto loans
-
Personal loans when you want certainty
🔄 What Is a Variable Interest Rate?
A variable interest rate (also known as a floating or adjustable rate) can change over time based on the performance of a benchmark interest rate—like the prime rate or LIBOR.
When the benchmark rises, so does your interest rate. When it drops, your rate (and payments) may decrease.
✅ Pros:
-
Lower initial interest rates
-
Potential to pay less if rates fall
-
Short-term savings
⚠️ Cons:
-
Unpredictable monthly payments
-
Risk of rising rates and higher total costs
-
Can lead to payment shock if rates rise quickly
Best for:
-
Short-term loans
-
Borrowers expecting rates to remain low
-
People who plan to pay off the loan early
🔍 Fixed vs. Variable: A Side-by-Side Comparison
| Feature | Fixed Interest Rate | Variable Interest Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Rate Stability | Stays the same | Changes over time |
| Monthly Payments | Predictable | Can increase or decrease |
| Initial Rate | Often higher | Often lower |
| Long-Term Cost | More stable | Could be more or less expensive |
| Risk Level | Low | Higher |
| Budgeting | Easier | More complex |
🧠 How to Choose Between Fixed and Variable Rates
Choosing between a fixed and variable rate depends on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and the loan type.
-
Go for a fixed rate if:
-
You need stable payments.
-
You’re taking out a long-term loan (like a 30-year mortgage).
-
You expect interest rates to rise in the future.
-
-
Choose a variable rate if:
-
You want to start with lower payments.
-
You’re borrowing short-term.
-
You’re comfortable with potential rate changes.
-
✅ Final Thoughts
Interest rates aren’t one-size-fits-all. Fixed rates offer stability and peace of mind, while variable rates can offer short-term savings—but come with more risk. Understanding how these rates work can help you make smarter financial decisions, save money, and avoid unpleasant surprises down the road.
Before you sign any loan agreement, make sure you ask:
-
Is the rate fixed or variable?
-
How often can it change?
-
What’s the maximum it could go up to?
The more you know, the better prepared you’ll be to choose the loan that fits your needs—and budget.