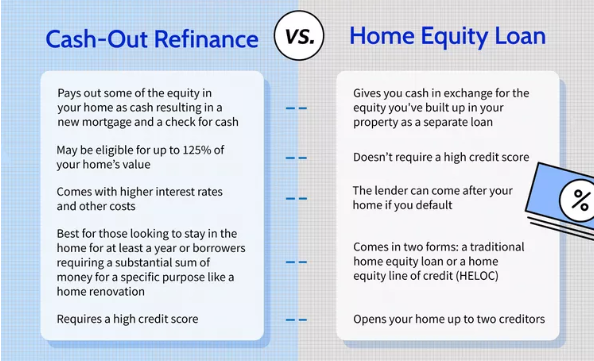
Cash-Out Refinance vs. Home Equity Loan: What’s the Difference?
If you’ve built equity in your home, you may be considering tapping into it to fund major expenses like home renovations, debt consolidation, education, or even a new investment. Two of the most popular ways to access your home’s value are a cash-out refinance and a home equity loan.
While they may sound similar, these options are quite different in how they work, how you repay them, and which situations they’re best suited for.
In this post, we’ll break down the key differences between cash-out refinancing and home equity loans, so you can choose the option that makes the most financial sense for you.
What Is Home Equity?
First, a quick refresher:
Home equity is the difference between your home’s market value and what you still owe on your mortgage. For example:
-
Home value: $400,000
-
Mortgage balance: $250,000
-
Home equity: $150,000
You can typically borrow up to 80%–85% of your home’s value (depending on your credit, lender, and loan type).
What Is a Cash-Out Refinance?
A cash-out refinance replaces your existing mortgage with a new, larger one. The difference between the two loans is given to you in cash.
Example:
-
Current mortgage: $200,000
-
New mortgage (after refinancing): $250,000
-
Cash-out amount: $50,000
✅ Pros:
-
May offer lower interest rates than home equity loans.
-
Consolidates your loan into one payment.
-
Can be used to switch loan terms or go from an adjustable to a fixed rate.
Cons:
-
You’re resetting your mortgage, which may mean paying interest longer.
-
Closing costs apply (typically 2%–5% of the loan amount).
-
If you recently locked in a low mortgage rate, refinancing could result in a higher rate.
What Is a Home Equity Loan?
A home equity loan is a second mortgage. You keep your original mortgage and take out a separate loan based on your home equity. It’s typically paid in a lump sum and repaid over a fixed term with a fixed interest rate.
Example:
-
Original mortgage remains unchanged at $200,000
-
Home equity loan: $50,000
-
Now you have two payments: one for your mortgage, one for your equity loan
✅ Pros:
-
Fixed interest rate and term = predictable monthly payments.
-
Great for large, one-time expenses (like a kitchen remodel or college tuition).
-
You don’t lose your original mortgage rate if it’s low.
Cons:
-
Creates a second monthly payment.
-
Typically comes with higher interest rates than a full refinance.
-
Also includes fees and closing costs.
Key Differences at a Glance
| Feature | Cash-Out Refinance | Home Equity Loan |
|---|---|---|
| Loan Type | Replaces existing mortgage | Second loan on top of current mortgage |
| Interest Rate | Usually lower | Usually higher |
| Monthly Payments | One combined payment | Two separate payments |
| Best For | Lowering rate & accessing cash | Keeping original loan, lump-sum need |
| Upfront Costs | Higher (closing costs) | Lower, but still includes fees |
| Loan Term | 15–30 years | 5–20 years |
Which One Is Right for You?
Ask yourself these questions:
✅ Choose a Cash-Out Refinance if:
-
You can secure a better interest rate than your current mortgage.
-
You prefer a single monthly payment.
-
You want to extend your loan term or change loan types.
-
You’re okay with resetting your mortgage clock.
✅ Choose a Home Equity Loan if:
-
You’re happy with your current mortgage rate and term.
-
You need a fixed sum of cash for a one-time project.
-
You can handle an additional monthly payment.
-
You don’t want to refinance your entire mortgage.
Bonus Tip: Don’t Confuse It with a HELOC
A Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) is another option that functions like a credit card secured by your home. It gives you flexible access to funds during a draw period. If you’re unsure whether you’ll need all the cash at once, a HELOC may be worth exploring.
Final Thoughts
Both cash-out refinancing and home equity loans can be valuable tools for leveraging your home’s value but they serve different purposes. Understanding the pros, cons, and costs of each will help you make an informed financial decision that aligns with your goals.
Before deciding, compare offers, review your credit profile, and speak with a trusted lender or financial advisor to determine which option fits your situation best.